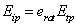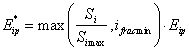Potential evaporation
In forests, evaporation of intercepted water may considerably exceed transpiration rates with equivalent local-climatic conditions.
When potential transpiration is used as a driving variable, i.e. for implicit big leaf simulations, a constant relation between wet surface evaporation rate and potential transpiration rate is assumed:
where erat is a parameter.
Otherwise the potential evaporation rate, Eip, from interception storage is calculated from the Penman combination equation assuming a surface resistance, rsint, representing the resistance to the single source point of the whole canopy, see eq.(3.12). See viewing function Potential interception evaporation.
The potential interception evaporation rate, Eip, is decreased if the water on the leaves does not cover the entire leaf, as determined by the parameter, ifracmin:
where Si is the interception storage and Simax is the interception capacity.
When the Penman combination equation is used to calculate Eip, the erat value is calculated with eq. (3.65), and used for example in eq. (3.67).