Partitioning of radiation between plants
When the single big leaf approach is used, the canopy is assumed to completely cover the soil surface. The partitioning of radiation between the plant canopy and the soil is then calculated according to Beer's Law (Eq. (4.1)).
If the multiple leaf approach is used each plant will have one big leaf which is considered to have a rectangular geometry (see Figure 4.3). The leaf is uniformly distributed within the total height of the canopy. A horizontal area extension and distribution is also assumed, which is described in detail in chapter “Plant water processes”. Each plant is considered to cover a fraction of the unit area of soil, distributed in one horizontal dimension around a central point xj. The horizontal and vertical distribution of plants results in a number of vertical, ∆Hi, and horizontal, ∆xk, zones as described in Figure 4.3.
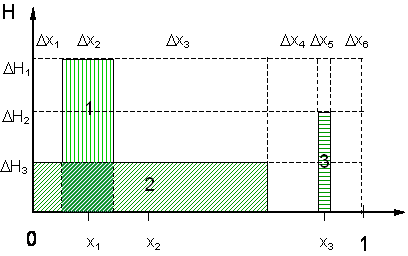
Figure 4.3. Geometric model used for partitioning of light between multiple plants.
The following equations, (4.67)-(4.71), can be used for short wave or net radiation. Thus, incoming radiation is denoted Rin, symbolising either Rn,tot or Rs, and absorbed radiation is denoted Rabs. The amount of absorbed radiation, Rabs, of a plant j in a height segment ∆Hi in the horizontal zone ∆xk is defined as:
where Rin.i,k is the radiation intensity above the height segment ∆Hi in the zone ∆xk and krn is the light use extinction coefficient given as a single parameter common for all plants. Al,i,j,k is the partial leaf area index of plant j in the specific zone, defined as:
where Al,j is the leaf area index defined as m2 leaf per unit area of soil, and fcc,j is the degree of surface canopy cover as defined above (cf. Eq. 3.10 in “Plant water processes”). Note that Eq. (4.68) implies that the leaf area index above the soil that is actually covered by the plant will be larger than Al,j, if fcc,j<1. See viewing function Beer’s Law.
The radiation intensity above a height segment i will be estimated as:
The fraction of light absorbed by vegetation above the unit area of soil, fcanopy, is defined by:
in the multiple plant case, and
if a single big leaf is used.
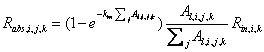
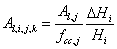
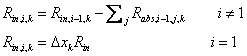
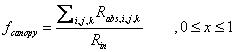
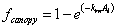
 Partitioning of long wave
radiation between plants
Partitioning of long wave
radiation between plants