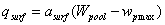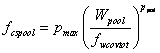Theory
The infiltration rate, qin, is a function of the infiltration capacity at the soil surface, icap, calculated from the saturated conductivity of the topsoil and the actual gradient in pressure head from the soil surface (ψ=0) to the middle of the uppermost layer according to Darcy’s law:
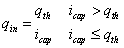 (2.16)
(2.16)
where qth is the throughfall of precipitation to the soil surface. In case of above surface irrigation, qth also includes the irrigation water; however, for all types of drip irrigation the water is directly transferred from the storage tank to the soil layers. If soil evaporation is greater than infiltration and the surface pool divided by the simulation time-step is greater than soil evaporation, an extra infiltration of water from the surface pool takes place. The amount of extra infiltration is equal to soil evaporation.
If throughfall exceeds the infiltration capacity a surface pool of water is formed on the soil surface. Water in the surface pool can either infiltrate with a delay into the soil or be lost as surface runoff. The surface runoff, qsurf, is calculated as a first order rate process:
where asurf is an empirical coefficient, Wpool is the total amount of water in the surface pool and wpmax is the maximal amount, which can be stored on the soil surface without causing any surface runoff. See viewing function Surface Runoff Function. If Wpool is smaller than wpmax then there is no surface runoff, qsurf,.
The fraction of the total soil surface that is covered with water, fcspool, is given by:
when the total amount of water is less than fwcovtot, which is a parameter value. See viewing function Ponded soil cover function.
During conditions with frost in the soil the saturated conductivity can be reduced because of the ice content in the soil (see “Influence of ice on water”).
A physical barrier for infiltration such as a roof can also be simulated by setting a value larger than zero for the iscov parameter.
Another special feature is the simulation of a furrow similar pattern on the soil surface (see switch Furrow). In this case a fraction, finfbypass, of the infiltration is going directly to the second compartment of the soil. This means that the top layer receives only 1-finfbypass of the total infiltration rate originating either from the surface pool or from precipitation.