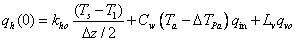Upper boundary condition
Calculation of soil surface heat flow, qh(0), requires special attention. Convective heat inflow is given by precipitation throughfall and/or snow melt multiplied by the relevant surface temperature and the heat capacity of liquid water (cf. eq. . (1.1)):
where kho is the conductivity of the organic material at the surface, Ts is the surface temperature, T1 is the temperature in the uppermost soil layer, ∆TPa is a parameter that represents the temperature difference between the air and the precipitation, qin, is the water infiltration rate, qvo is the water vapour flow and Lv is the latent heat. The temperature difference, Ta - ∆TPa, can optionally be exchanged to surface temperature, Ts (see switch PrecTemperature).