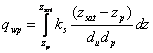Linear equation
In the simplest physically based approach (“linear model”), the horizontal flow rate, qwp, is assumed to be proportional to the hydraulic gradient and to the thickness and saturated hydraulic conductivity of each soil layer:
where du is the unit length of the horizontal element i.e. 1m, zp is the lower depth of the drainage pipe i.e. the drainage level, zsat is the simulated depth of the ground water table and dp is a characteristic distance between drainage pipes. Note that this is a simplification where the actual flow paths and the actual gradients are not represented. Only flows above the drain level zp are considered. See viewing function Physically based drainage equation.
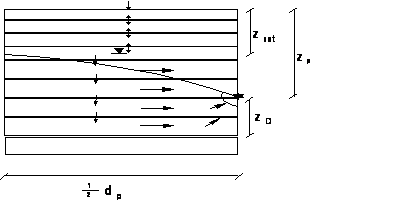
Figure 2.6. The geometrical assumptions behind the groundwater flow towards a sink point in the saturated zone of the soil.